What are the methods of electroplating? What is the difference between white zinc plating and color zinc plating?
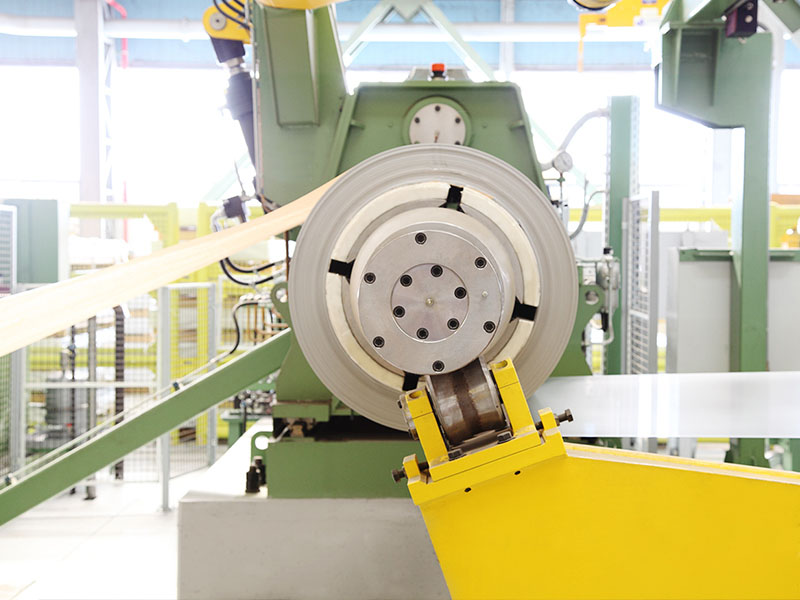
Electroplating is the process of applying electrolysis principle to coat a thin layer of other metals or alloys on some metal surfaces. It is the process of using electrolysis to attach a layer of metal film to the surface of metal or other materials to prevent metal oxidation (such as corrosion), improve wear resistance, conductivity, reflectivity, corrosion resistance (copper sulfate, etc.), and improve aesthetics.
Basic Principles of Electroplating
During electroplating, the coated metal or other insoluble materials are used as anodes, the workpiece to be plated is used as cathode, and the cations of the coated metal are reduced on the surface of the workpiece to be plated to form a coating. In order to eliminate the interference of other cations and make the coating even and firm, it is necessary to use the solution containing the coating metal cations as the electroplating solution to keep the concentration of the coating metal cations unchanged.
The purpose of electroplating is to coat the substrate with a metal coating to change the surface properties or dimensions of the substrate. Electroplating can enhance the corrosion resistance of metals (most of the coated metals are corrosion-resistant metals), increase hardness, prevent abrasion, improve conductivity, smoothness, heat resistance and beautiful surface.
Due to different environments, the coating requirements are different. For example, ferrous metal parts are usually protected with zinc coating under general atmospheric conditions, and cadmium coating under marine climatic conditions. When the coating is required to be thin and has strong corrosion resistance, tin cadmium alloy can be used to replace cadmium coating; Marine instruments made of copper alloy can be protected by silver cadmium alloy; Ferrous metal parts in contact with organic acids, such as food containers, are protected by tin plating, which is not only strong in corrosion resistance, but also harmless to human health.
 JIMI STEEL MILL LIMITED
JIMI STEEL MILL LIMITED


